Problem
How to learn complex relationships between different tasks.
Key Ideas
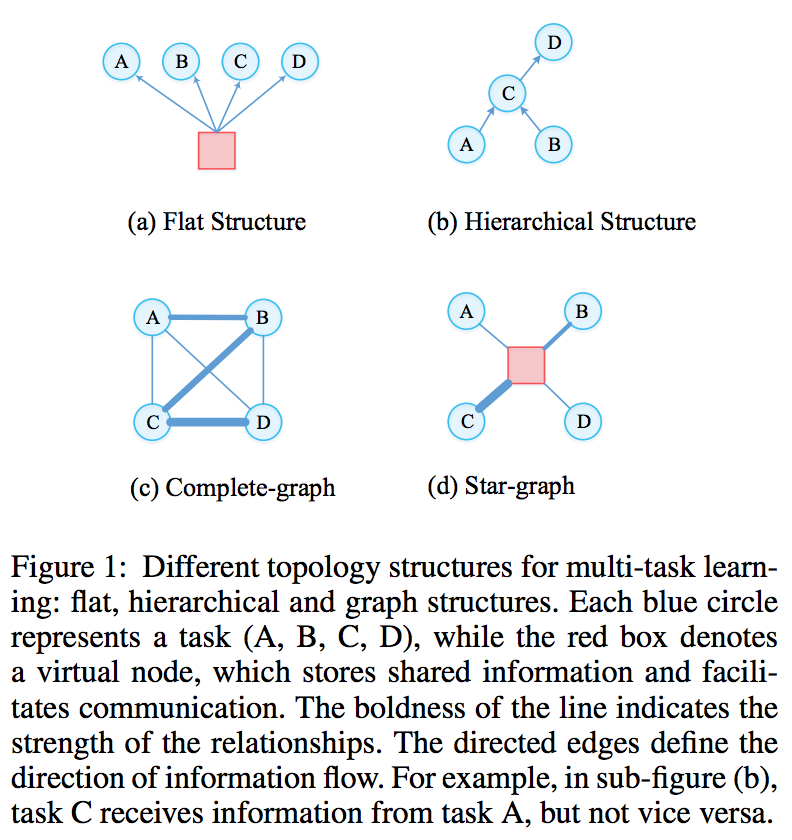
- Instead of use flat structure or pre-defined hierarchical structure, learn a complete graph or star graph between tasks. It is weighted directed graph.
- Tasks are nodes in a task graph. Interactions between words are modeled by LSTM, and interactions between tasks are modeled by GCN.
- Relationship between tasks depend on the specific sample and context, not static scores.
- In Star-graph, utilize gating mechanism to aggregate different information from different tasks. Use an extra LSTM as virtual node to aggregate all task information.
Model
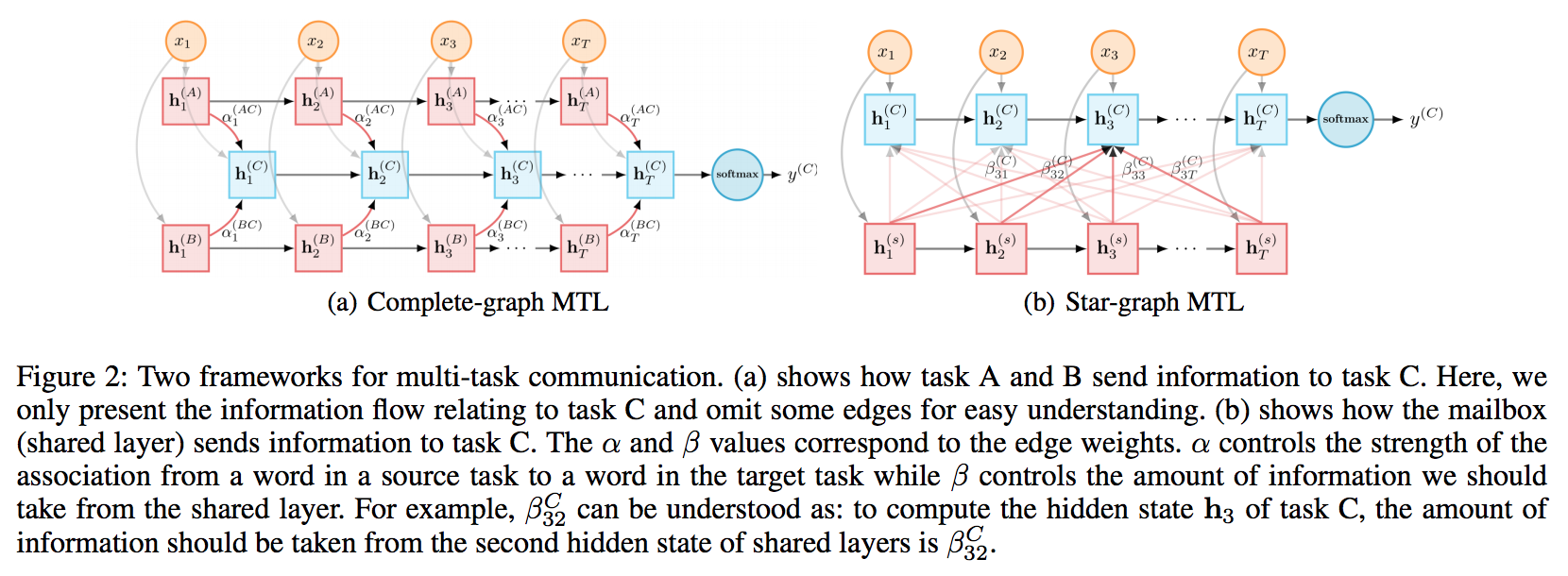
-
For complete-graph, learn weights from other tasks to target task. The weights are depending on the current inputs. The weights are used to get an aggregated vector from other tasks. It will be used in the updating of target task’s LSTM.
-
For star-graph, use an extra LSTM as virtual node. It acts like a mailbox. Different tasks share the same LSTM and input their specific input. Therefore, it produces different outputs for each task. The weights are learned in a similar way. Star-graph has smaller calculation complexity.
-
Training
Jointly train multi-tasks with weighted loss function.
Performance
The joint model shows significant benefits over single models.
Comments
- Whether it is too complicated to learn different weights for each different input?
- Can we just learn a relationship matrix between different tasks?
- The gating mechanism in Star-Graph is reasonable.
Reference
Paper link: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1811.10211.pdf
