Introduction
The emergence of BERT brought NLP into a new era. Recent research works usually apply a similar “pre-training + finetuning” manner. In this post, we briefly summarize recent works after BERT. Some of them improves BERT by introducing additional tricks, training objectives. Some of them unify different tasks in the same framework. And some propose new ideas to handle the drawbacks in BERT.
Pre-Training with Whole Word Masking for Chinese BERT
Problem
Improve BERT with whole word masking. Applied to Chinese BERT.
Key Ideas
Instead of random masking in original BERT, it masks whole words. This trick is named whole word masking, and is also utilized in ERNIE.
Different with ERNIE, it just use word segment. No extra knowledge.
Model
The model is same with BERT-Base for Chinese.
The Whole Word Masking is illustrated by the following figure.

Comments
This word combines whole word masking with word segmentation. It tests different Chinese NLP tasks to show the benefit. It also provides multiple tips for model training and so on.
ERNIE: Enhanced Representation through Knowledge Integration
Problem
Feed our knowledge about entities or phrases into BERT.
Key Ideas
Applied 3 different masking strategies: token masking, entity masking, phrase masking.
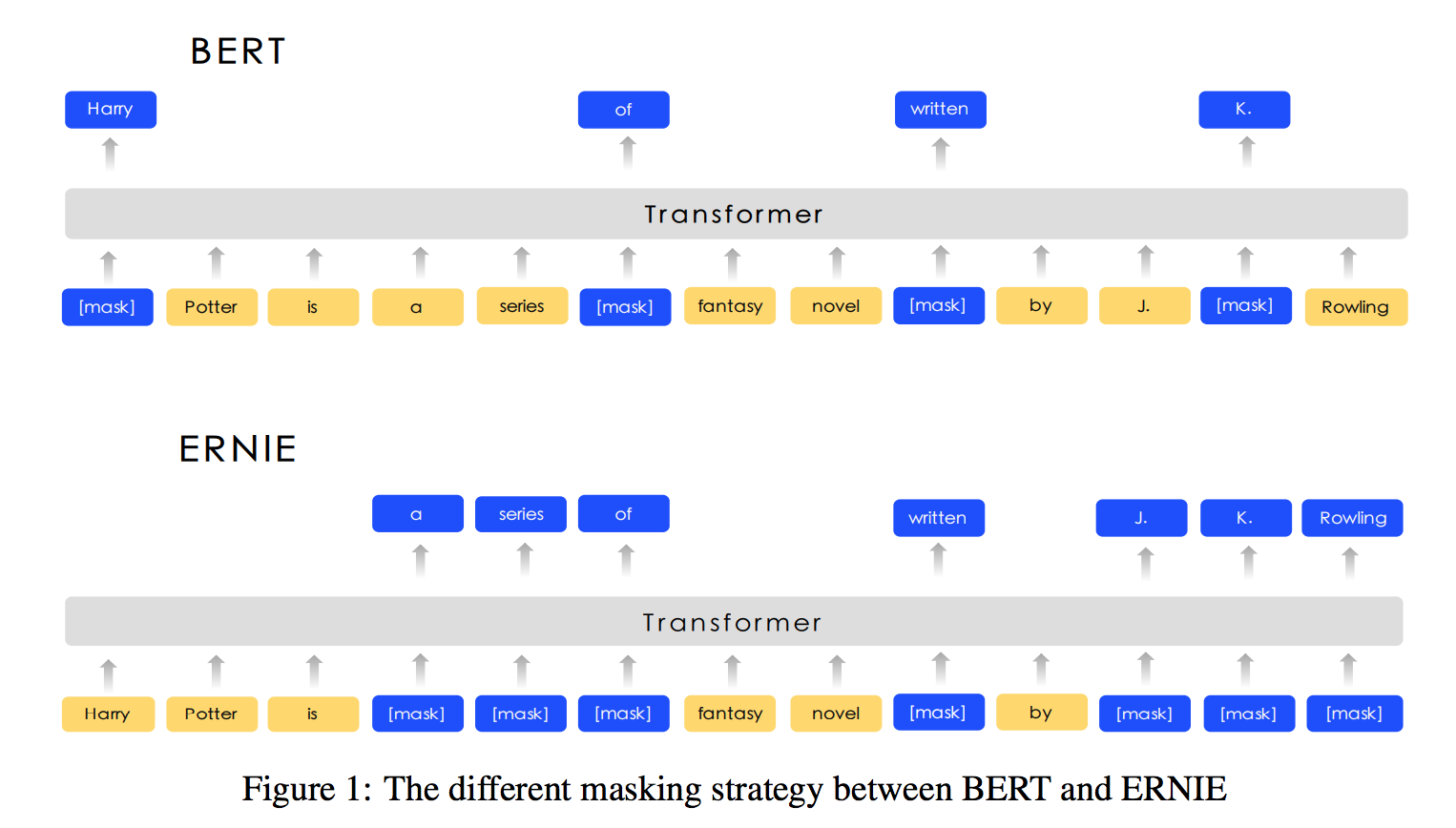
Model
Same as BERT-Base. Utilized word/phrase segmentation for different languages. Use extra knowledge about entities, phrases.
Apply multi-stage knowledge masking strategy to integrate phrase and entity level knowledge into the language representation.

For data, it utilized different datasets: Wikipedia, Baidu Baike, Tieba, etc.
Comments
- Knowledge about words, entities, phrases, and maybe higher levels, is useful.
- We can try to make the model learn the boundaries for different semantic levels. We can also make extra knowledge be ealisily pluged in.
- Use different datasets.
Cross-lingual Language Model Pretraining
Problem
Learn cross-lingual language models (XLMs).
Key Ideas
- unsupervised monolingual pretraining.
- supervised cross-lingual language modeling.
Specificly, it applies the following training objectives.
-
Language Modeling
This is traditional left-to-right language modeling task.
-
Masked Language Modeling
Same with BERT. Difference is that it use random text streams of random umber of sentences (truncated at 256 tokens) instead of sentence pairs as input.
-
Translation Language Modeling
This is key to cross-lingual language modeling. Here the input is the concatenation of parallel sentence pairs in different languages. And we randomly mask some tokens in both sentences. The objective is predicting the masked tokens.
For embedding, it process all languages with the same Byte Pair Encoding vocabulary.
Model
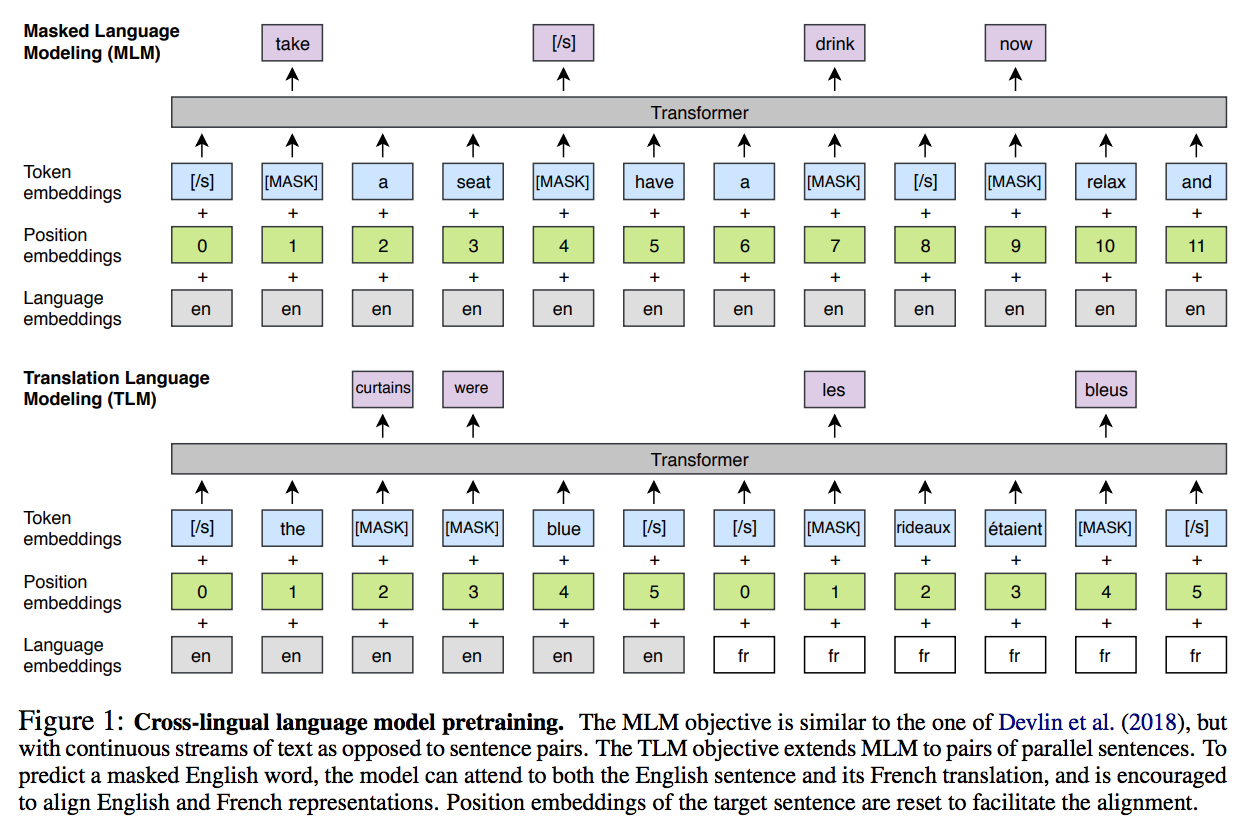
Same structure with BERT.
Comments
Basically, this work shows utilize resources from different languages are helpful. It is a cross-lingual version BERT.
MASS: Masked Sequence to Sequence Pre-training for Language Generation
Problem
Adapt BERT to sequence2sequence for text generation tasks.
Key Ideas
- Use unsupervised prediction task: mask a continuous sequence fragment in input, predict the masked fragment by seq2seq model.
- BERT and GPT models are considered as special cases of MASS: mask length k=1, similar with BETT; mask length k=m (input sentence length), same with GPT.
Model
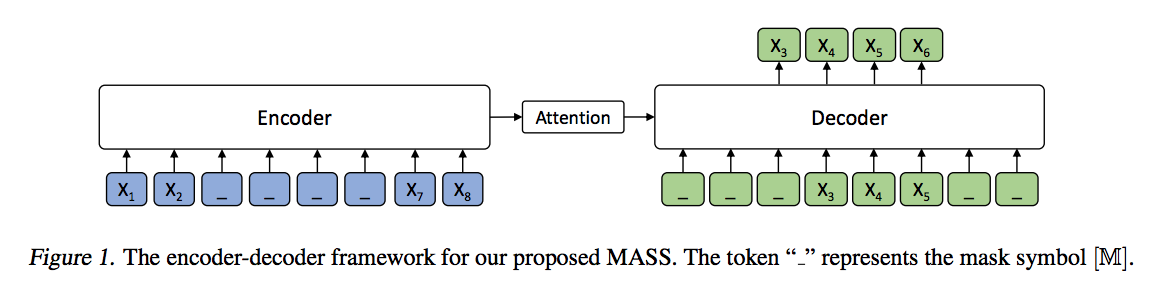
Encoder-Decoder structure. 6-layer transformers for both encoder and decoder.
Comments
This work adapts BERT idea to generative tasks by jointly training both encoder and decoder in a seq2seq framework.
It tells a good story by showing BERT and GPT as special cases of MASS.
The proposed model are more powerful for generative tasks.
Unified Language Model Pre-training for Natural Language Understanding and Generation
Problem
Unify different language modeling tasks in the same manner.
Key Ideas
- Unifying different pre-training tasks for both language understanding and generation.
- Combines unidirectional (like ELMo, GPT), bidirectional (like BERT), seq2seq prediction (like MASS) training objectives.
- Train one same Transformer-based model (structure like BERT). Use different attention masks for different tasks. This is the key to unifying different tasks: it is just different attention masking strategy! It uses different mask matrices to control what context a token can attend to when computing its contextualized representation.
Model
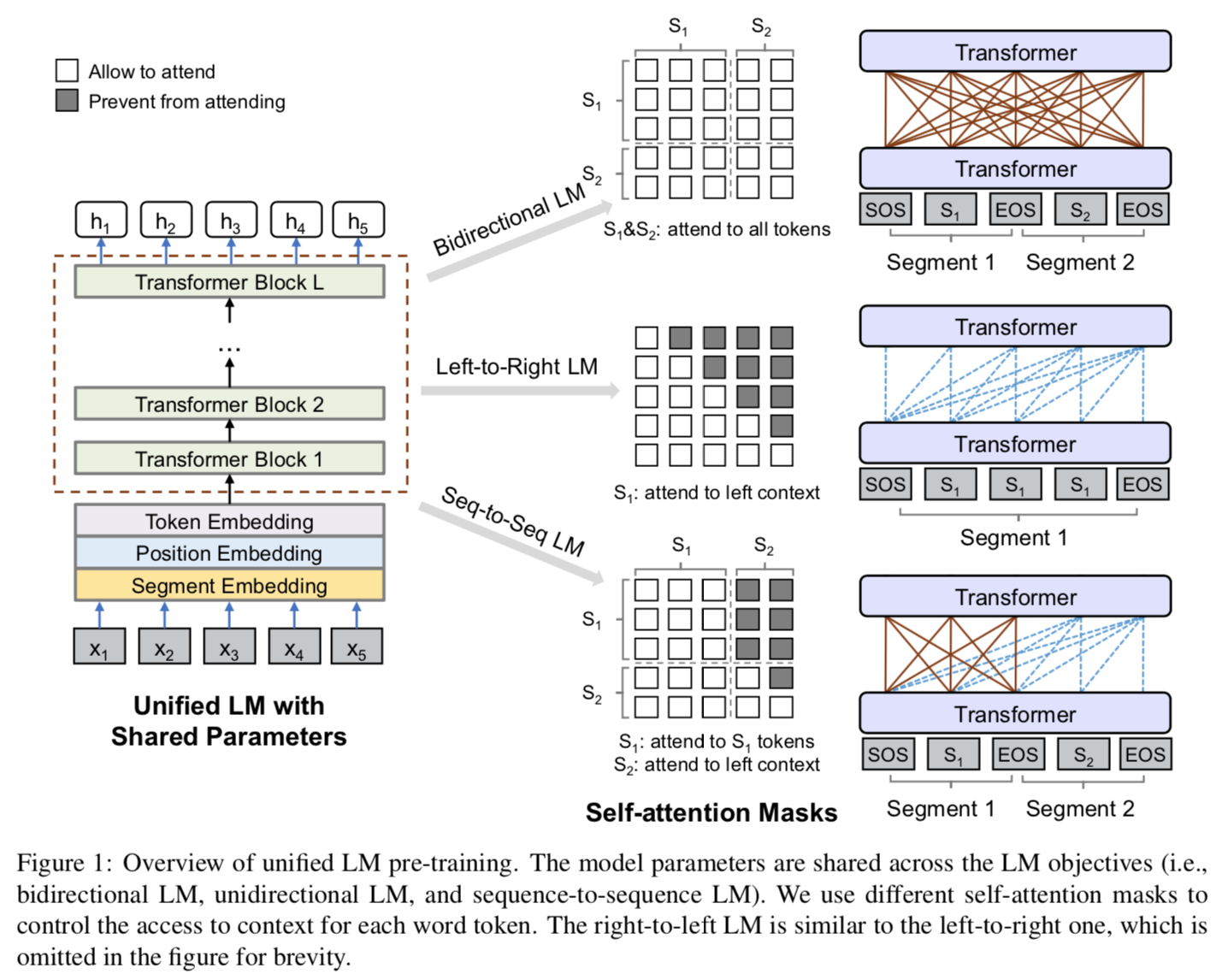
Same model structure with BERT. Same input representation.
Different mask matrices for different training objectives.
Share the same Transformers. Use BERT-large to initialize model parameters.
Comments
The idea of unifying different tasks using self-attention masks are good. Essentailly, different language modeling tasks vary in what context we can see during pre-training. By incorporating different tasks using the same model, the model is able to perform both NLU and NLG tasks, while original BERT are mostly good at NLU and not as good for NLG tasks.
XLNet: Generalized Autoregressive Pretraining for Language Understanding
Problem
Solve the limits in BERT.
Key Ideas
The limits in BERT:
- Neglects dependency between the masked positions.
- Pretrain-finetune discrepancy due to MASK.
- Auto Encoding (AE) objective, not Auto Regressive (AR) objective, therefore not powerful enough for generative tasks.
Changes in XLNet:
- Use Permutation Language Modeling as training objective: sample different sequences for the same sentence. Therefore, the model can both see previous words and see contextual words in different sampled sequences. This helps to combine the benefits of both AR and AE. Note that the permutation only permutes the factorization order, not the sequence order.
- Use Two-Stream Self-Attention: the query attention is actually contextual representation for each token, it only contains the information from contextual words and its current position; the content attention is content representation, it contains all the contents information in context words and current position word.
- Use Transformer-XL: the relative-position encoding and segment-recurrence mechanism helps to model long text. Details can be found in the Transformer-XL paper.
Model
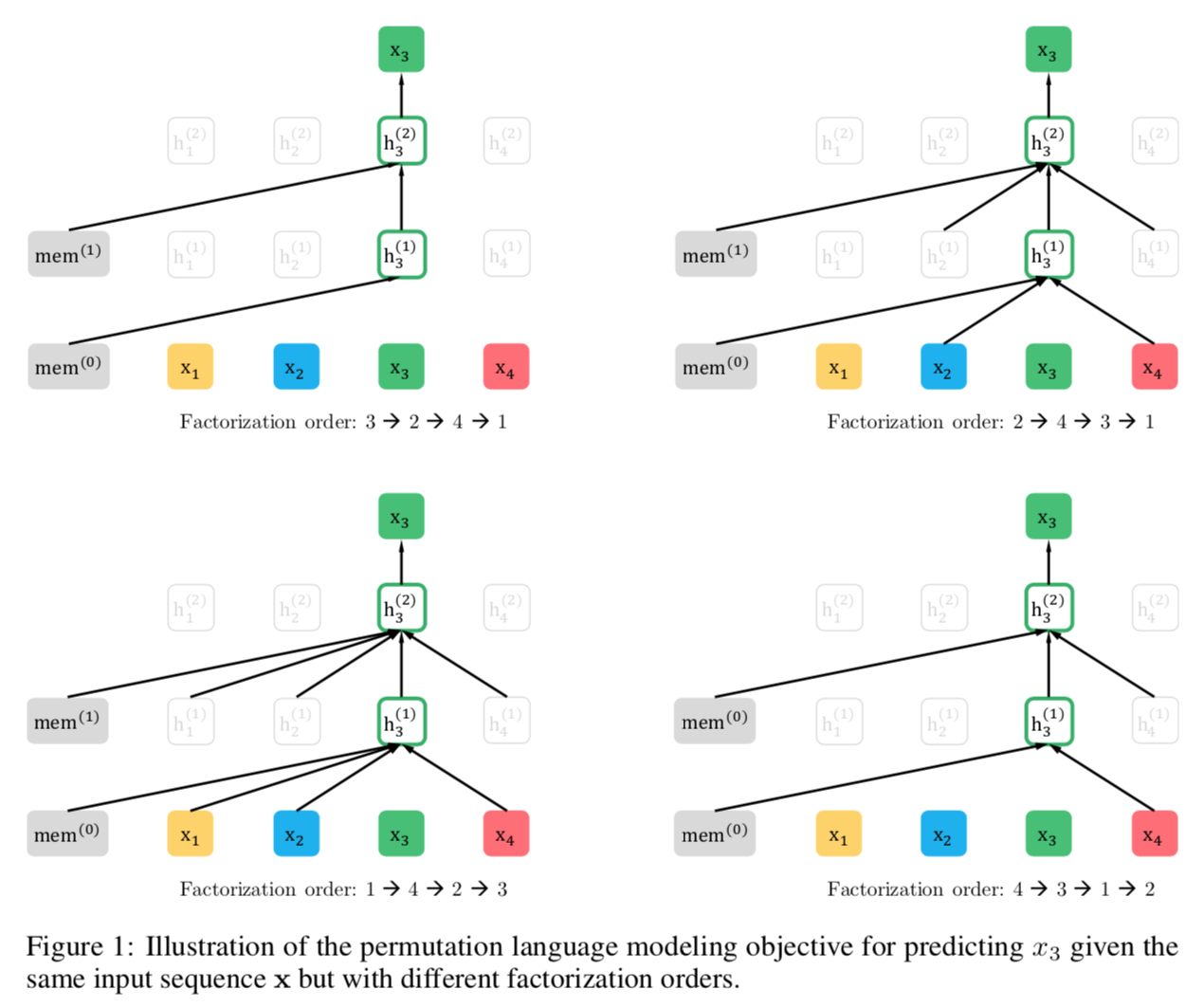
Above shows permutation language modeling. Notice that when we predict the next token, we will have position information to tell us which postion we are predicting.
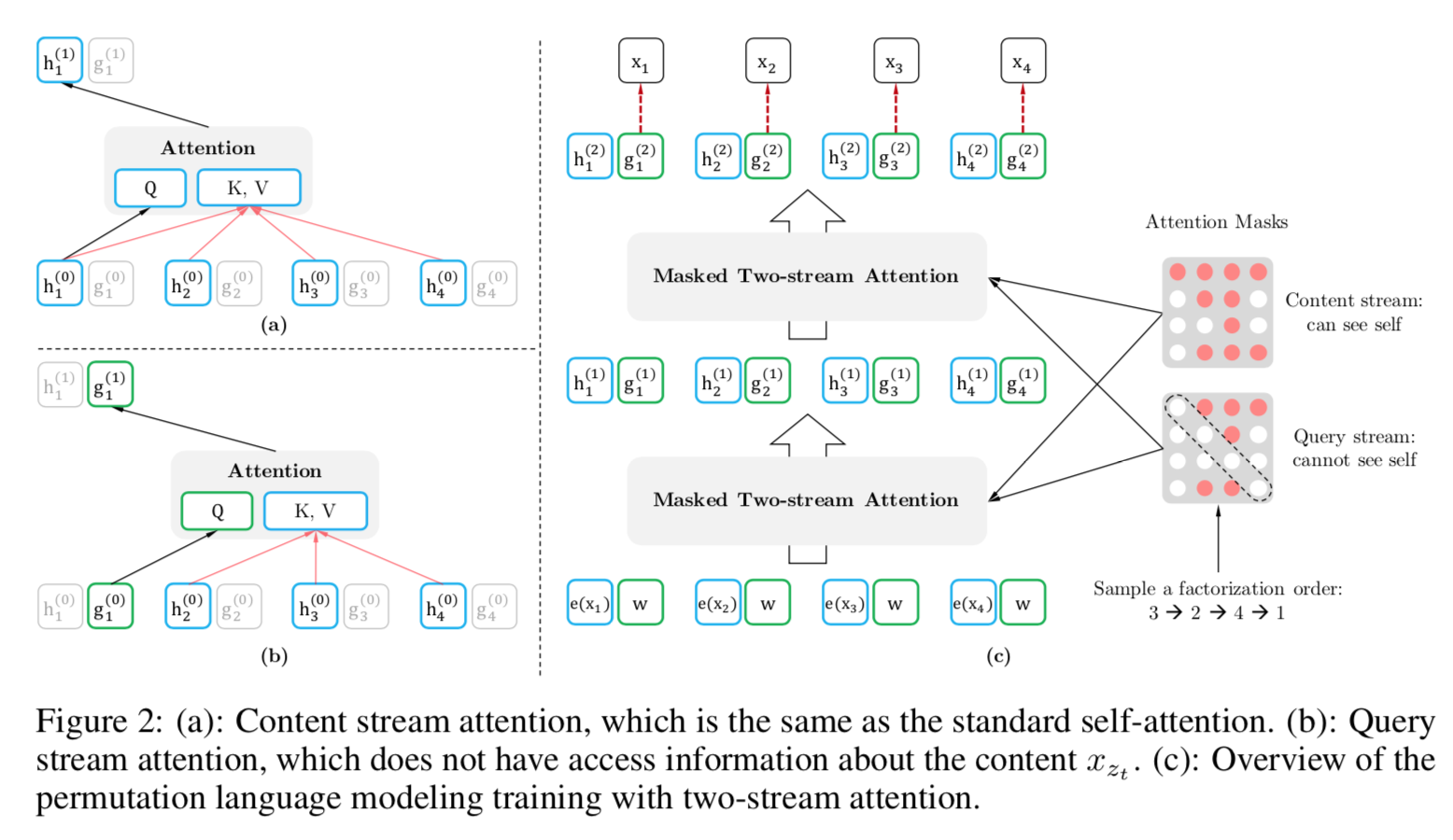
Above shows how masked two-stream self-attention mechanism works. The mask controls what context words each position can attend to.
Comments
Basically, XLNet tries to improve the pretraining stage of BERT. Its ideas combines the benefits from both AR-based models (such as GPT, GPT-2) and AE-based models (such as BERT). At the same time, it is also harder to train. Its model size is bigger, and utilized more training corpus and TPUs.
Summary
We can see that, these tasks are trying to improve BERT from different aspects:
- ERNIE Better masking strategy: mask entities or phrases or whole words.
- XLM Cross-lingual BERT: incorporate parallel sentences as supervised training objective.
- MASS Seq2Seq for generation: masked language modeling.
- UNILM Unifying understanding and generation tasks: add different language modeling tasks and utilize mask matrices for different tasks. Share the same encoder for different tasks.
- XLNet Design new permutation language modeling tasks to combine AR and AE model benefits. Use masked two-stream self-attention and compute two representation for each token. Incorporating Transformer-XL to modeling long text.
Combining different pre-training objectives (or tasks), utilizing mask matrices, better transformer for long text, cross-lingual datasets, etc., these ideas are key to these models.
References
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/65346812
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/68295881
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/68362016
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/70257427
https://www.jiqizhixin.com/articles/2019-06-29-3
