Introduction
Automatically evolving a network structure for handling different tasks is an important research problem. Here we summarize a few works.
Learn to Grow: A Continual Structure Learning Framework for Overcoming Catastrophic Forgetting
Problem
Handling catastrophic forgetting problem in continuous learning by learning to grow network structure for different tasks.
Key Ideas
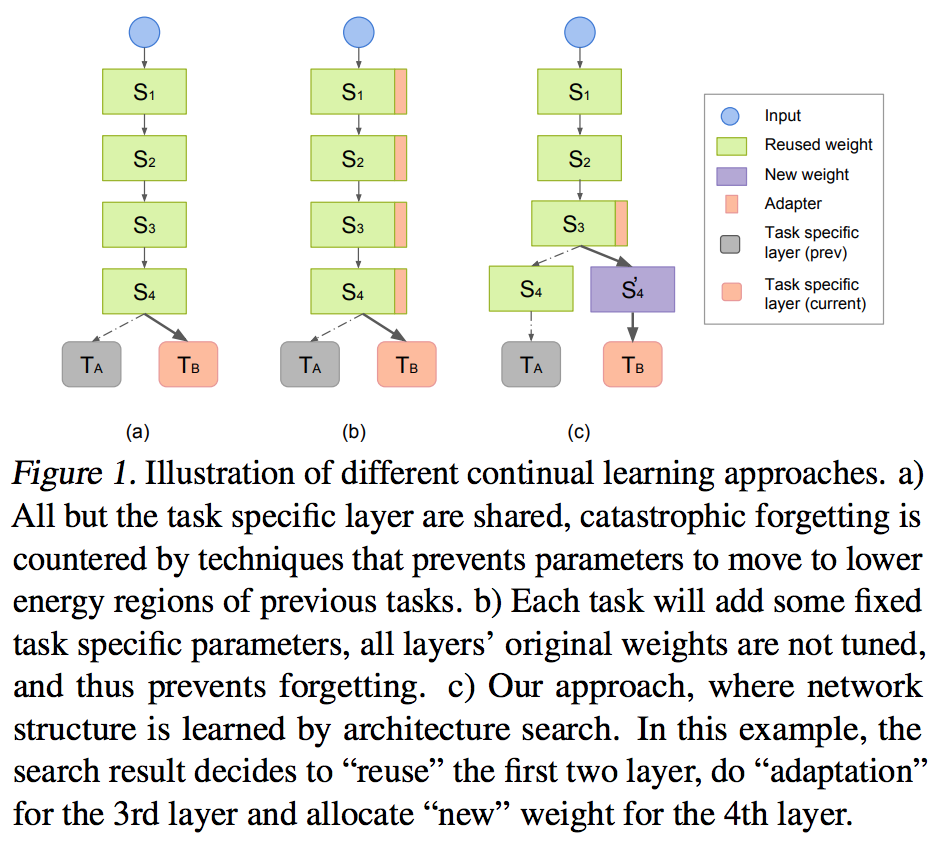
- Employ Neural Architecture Search (NAS) for structure optimization.
- Given a new task, the goal of search is to seek the optimal choice for each layer: reuse, adaptation, and new. Reuse operation shares the same layer for a new task, adaption operation adds a small parameter overhead that trains an additive function to the original layer output. New operator spaws new parameters of exactly the same size of the current layer parameters.
- Optimize structure and parameters alternatively.
Model
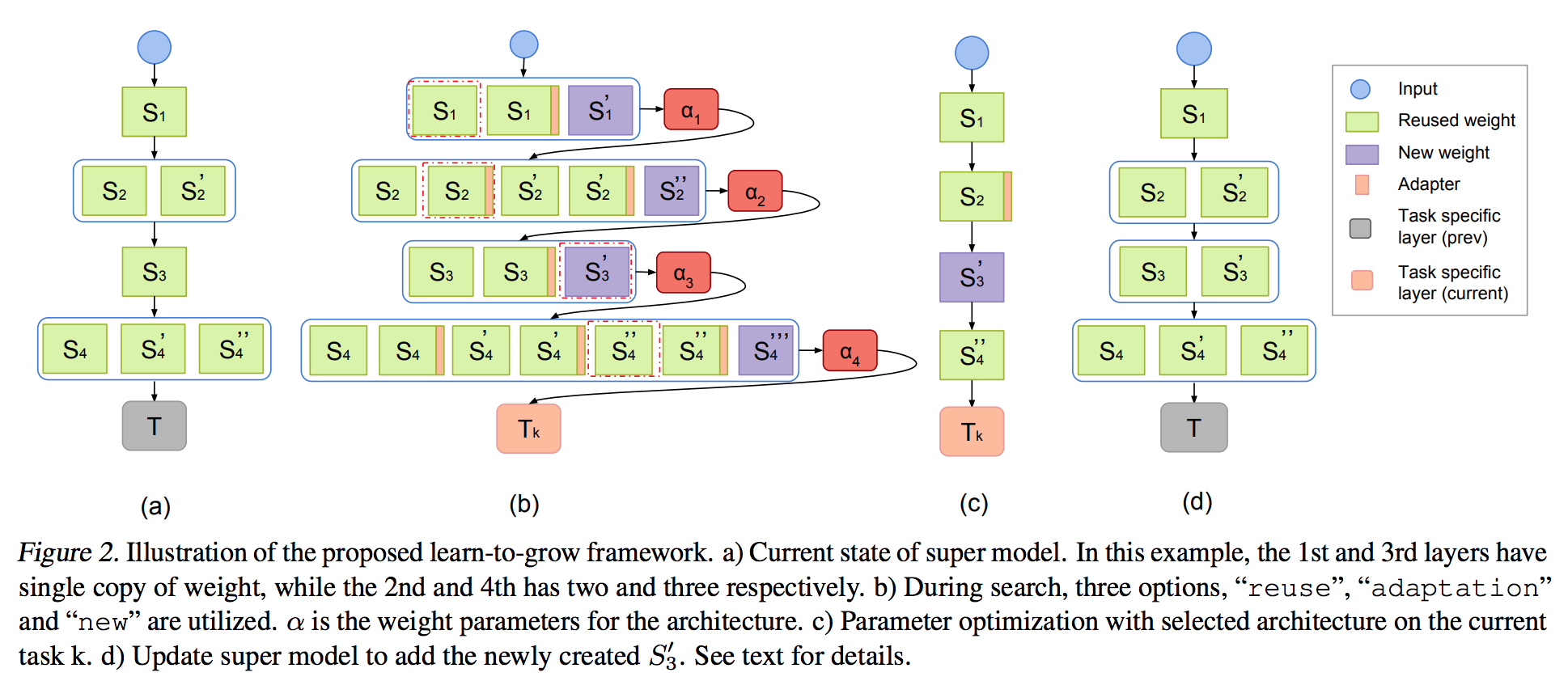
Relax the categorical choices of each layer as a Softmax over all possible choices. Then discrete search of architecture is posed as optimizing a set of continuous architecture weights.
After search, we select the choice with the maximum weight for each layer.
Comments
In this work, the optimization of architecture and parameters are seperated. For new tasks, it tries to select an action for each network layer. We can see it is growing a network horizentally, by applying NAS with different operators: reuse, adapt, and new.
Instead of just update a network horizentally, we can vertically grow it at the same time. In this way, we can both adapt an existing layer (or expand the width) and growing the depth by adding more layers. This can be unified by adding more operators into the learn-to-grow framework.
AutoGrow: Automatic Layer Growing in Deep Convolutional Networks
Problem
Automatically depth discovery in Neural Networks.
Key Ideas
- Neural Architecture Search, Neural Evolution, etc., they require tremendous computing resources. This work focuses on growing network by depth.
- Use “network - sub networks - sub modules - layers” to describe the architecture hierarchy.
- Initializer, grow policy, stop policy. These 3 components are the keys in autogrow.
Model
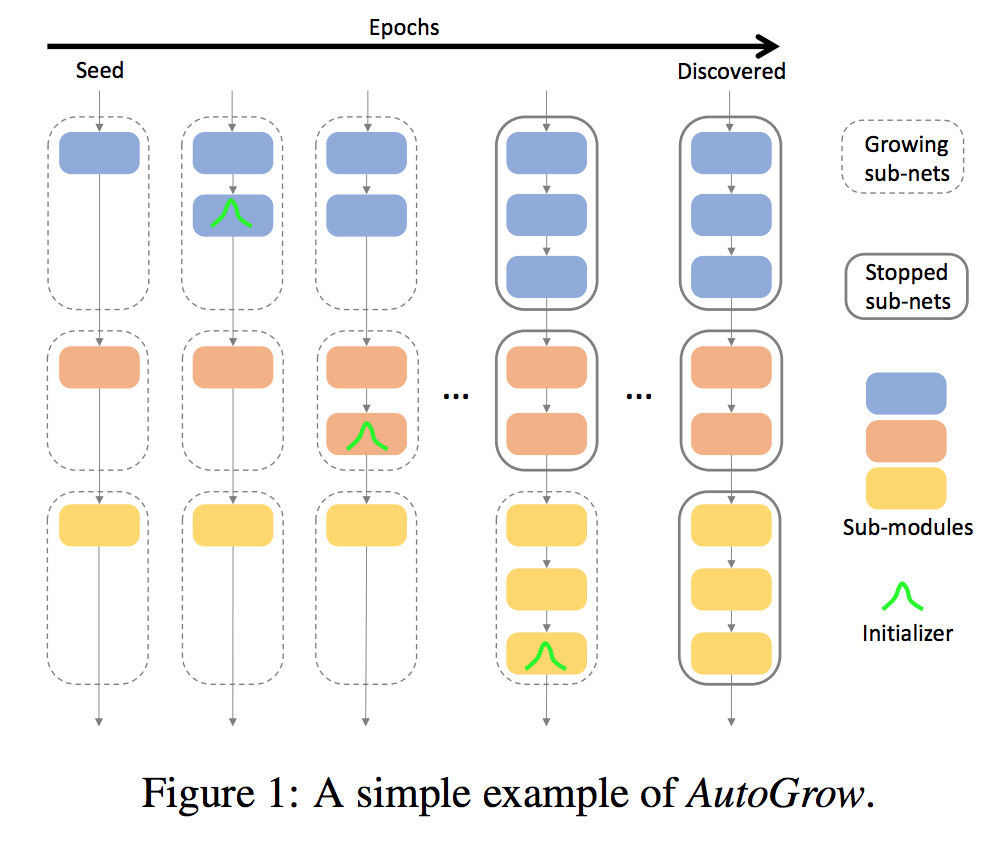
- Initializer: decides how to initialize a new layer. The paper tried ZeroInit, AdamInit, UniInit and GauInit. GauInit gives the best result in experiments.
- Growing policies: Morphing Growth keeps growing network when current network converges. Periodic Growth always grows every K epochs.
- Stopping policies: Morphing Stop stops growing if the accuracy improvement is less than a threshold in the first J epochs after adding new layer. Periodic Stop stops growing when the improvement is less than a threshold for the last J epochs. For Morphing strategy, usually set K=J. For Periodic strategy, K < J.
- A key result found in experiments is that periodic strategy gives better result than morphing strategy. The hypothesis is that: a fully converged shallower network is an inadequate initialization to train a deeper net.
Note that the word “Morphing” means that a child network with different architecture produces the same output with a parent network for the same input, or its network function can be completely preserved.
Comments
Basically, to grow the depth of a network, the key problems are how to initialize new layers, and when to grow or stop.
We can combine Learn-to-Grow and AutoGrow to make the network structure evoluation more flexible, unified, and controlled. First, more operators can be added ito the framework; second, for each operation, such as adaption or depth grow, how much to grow can also be determined.
Besides growing width and depth, more generally neural architecture search can be applied. How to grow a network to handle different tasks with out catastrophic forgetting is an interesting problem. Therefore, neural architecture, evolutional learning, meta-learning, and continuous learning (0r lifelong learning) are research topics we shall pay attention to.
References
Learn to Grow: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1904.00310.pdf
AutoGrow: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1906.02909.pdf
Network Morphism: https://arxiv.org/abs/1603.01670
